VIBRATION AND VIBRATION METERS
Simple Diagnosis
Simple diagnosis is one of the methods of equipment diagnosis, and is a technique to quickly and easily determine the condition of equipment.
The methods of grasping the condition based on the amplitude of vibration can be carried out without specialist knowledge.
The judgment based on the crest factor (C.F.) is an index that shows the impact of a waveform and is defined by the ratio of the effective value to the peak value.
The judgment criteria used in the maintenance of mechanical equipment include "Absolute judgment criteria", "Relative judgment criteria", and "Mutual judgment criteria".
Vibration magnitude
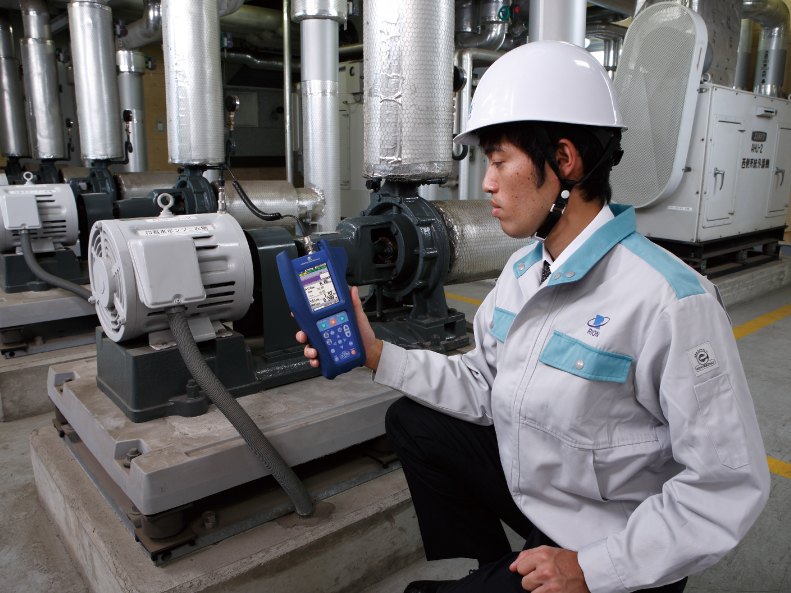

Measuring the magnitude of vibrations is a useful diagnostic technique for ascertaining that machinery is operating normally and checking for signs of possible problems.For example, when vibrations exceeding the reference value in the velocity range (up to 1 000 Hz) are detected, the presence of an imbalance, misalignment, or loosening condition can be suspected, whereas vibrations in the acceleration range (1 kHz to about 12 to 15 kHz) point to possible bearing or gear problems.
Crest factor
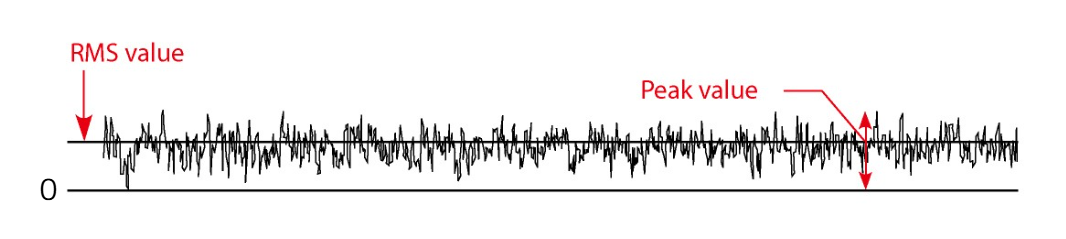
↑ Normal bearing(Peak value / RMS value = crest factor is small)
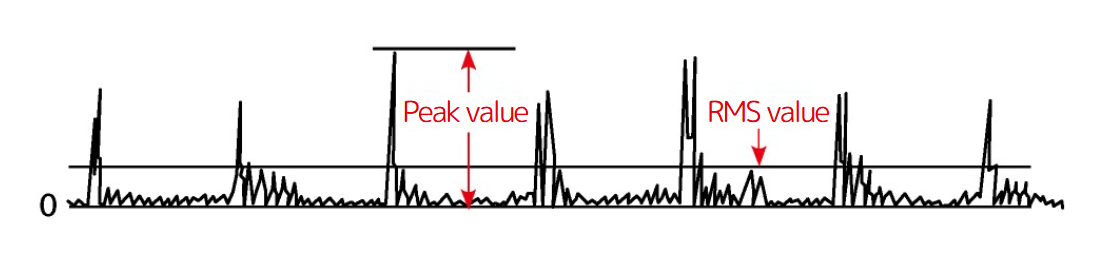
↑ Bearing with spot damage(Peak value / RMS value = crest factor is large)
The crest factor (C.F.) is an indication of the impact characteristics of a waveform. It is determined by the ratio between the RMS and peak values.Higher crest factor values indicate a stronger impact quality. The crest factor of acceleration measurements is useful for detecting the early stages of bearing damage.
Crest factor = Peak value/RMS value
The vibration waveform of a bearing with a fault in the initial stage is shown in the example below. Compared to the waveform of a normal bearing, the crest factor is higher.
Maintenance Management of Machine Equipment
By periodically measuring the vibration magnitude and comparing the results to a reference value, the equipment condition (normal or potential problem) can be diagnosed.
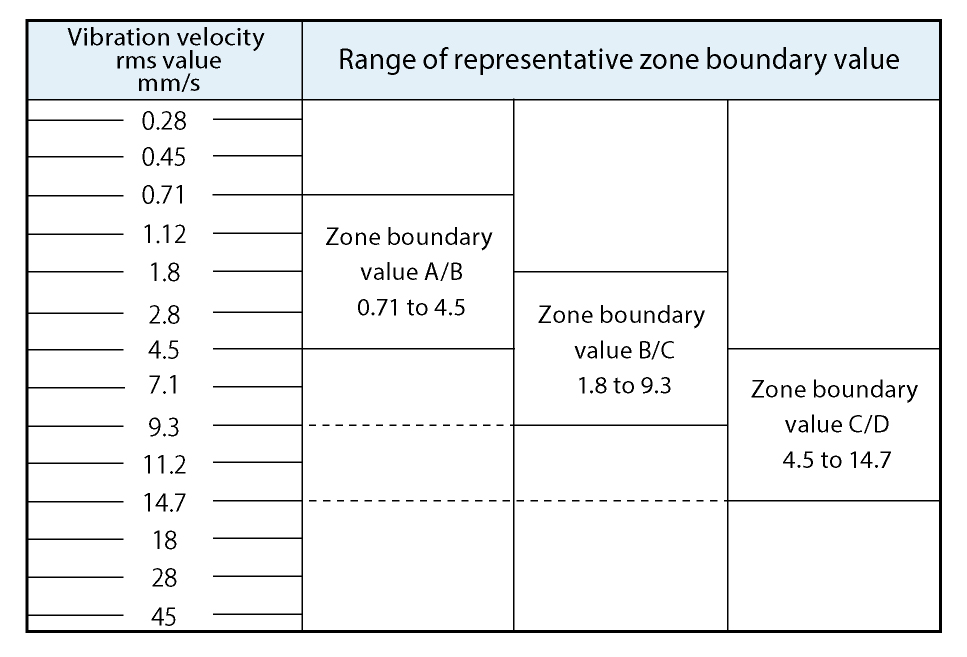
Using an absolute evaluation standard
ISO 20816 series (Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non-rotating parts). According to ISO 20816-1:2016, evaluation criteria for mechanical vibration over a specified range are to be decided by agreement between the supplier and the user of the machine, and boundary values for evaluation are to be determined in consideration of the measurement position and the support rigidity of the machine etc.
A: Newly installed machinery will normally be within this range.
B: Long-term continuous operation allowed.
C: Long-term continuous operation not allowed,
but limited-term operation allowed.
D: High risk of injury. Operation not allowed.

Using a relative evaluation standard (trend management)
Judgement is based on the rate of change relative to the initial value of vibration magnitude.
In order to understand the cause of abnormal vibrations that change in vibration state, such as in rotating equipment, it is necessary to accumulate measurement data and manage the vibration state.
Baseline values are determined from accumulated measurement data, and alarm and stop values are determined.
If the alarm value is exceeded, monitoring is strengthened, and if the stop value is exceeded, a detailed diagnosis is performed.In trend management, it is desirable to monitor the magnitude of vibration value, the magnitude of change in vibration value, and the speed of change in vibration value. Generally, in the vibration speed range, the alarm value is set to 2 to 3 times the reference value, and the stop value is about 10 times the reference value.
The vibration measurement part, measurement direction, and measurement period of the machine are determined, and a graph (trend management graph) is created and managed with the measured values written in chronological order.
●Judgment criteria values
- Baseline: When the machine is in operation for a certain operating time, it shows a stable vibration value in a steady operating state. Vibration value obtained empirically in this way.
- Alarm: When the vibration value reaches a certain value or a significant change in the vibration value is detected, an alarm is issued that requires some kind of action. Even if the warning value is exceeded, operation can continue for a certain period of time. Approximately 2 to 3 times the reference value (empirical value), individual differences depending on the machine.
- Stop (Trip value): The magnitude of vibration that may cause damage if the machine continues to operate. Approximately 10 times the reference value (empirical value), individual differences between machines are not recognized.
Mutual judgment criteria
If there are multiple pieces of equipment with the same specifications, they are compared to each other to evaluate them.






